Galeria de imagens
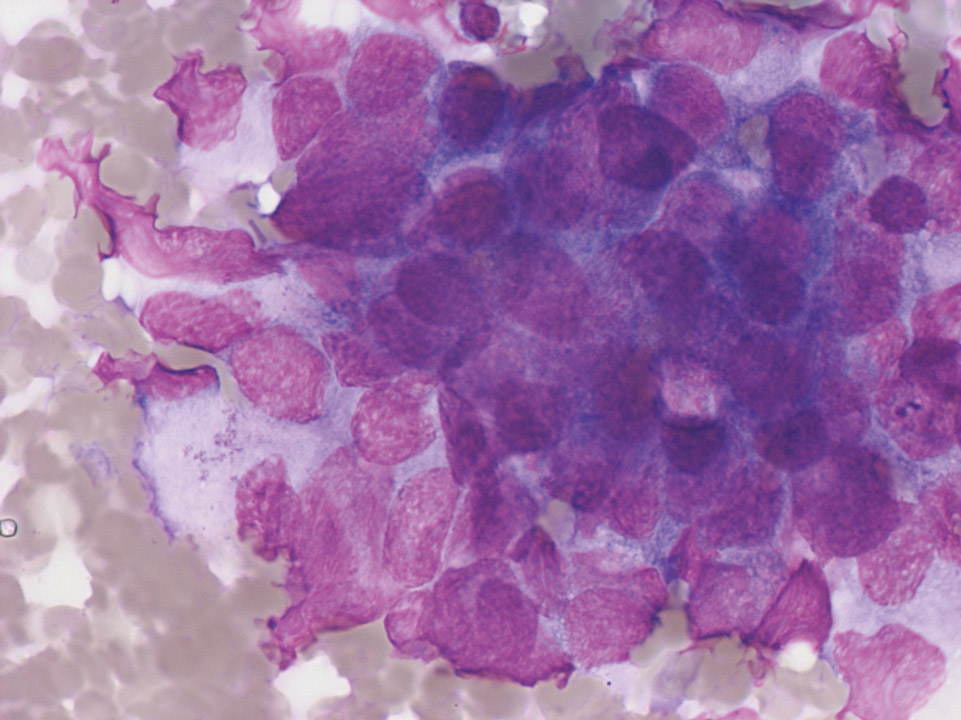
Lymphoma cells in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytospin preparation. Patient diagnosed with localised diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: monoclonal B cell population with the following flow cytometric results CD19+, CD20+, CD38+, CD5-, Lambda+, Kappa-. May-Gruenwald Giemsa stain.
<p>Lymphoma cells in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytospin preparation. Patient diagnosed with localised diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: monoclonal B cell population with the following flow cytometric results CD19+, CD20+, CD38+, CD5-, Lambda+, Kappa-. May-Gruenwald Giemsa stain. </p>
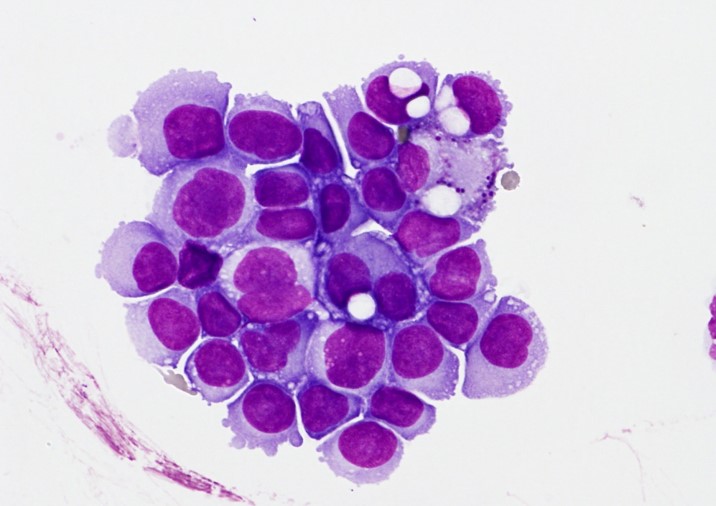
This cytospin prepared from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is rich in cells which are malignant epithelial tumour cells. They have polymorphic hyperchromic nuclei and sometimes there are double nuclei seen. Some cells have vacuolated cytoplasm, sometimes with magenta bodies. Patient know with breast cancer and hydrocephalus. May-Gruenwald Giemsa stain.
<p>This cytospin prepared from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is rich in cells which are malignant epithelial tumour cells. They have polymorphic hyperchromic nuclei and sometimes there are double nuclei seen. Some cells have vacuolated cytoplasm, sometimes with magenta bodies. Patient know with breast cancer and hydrocephalus. May-Gruenwald Giemsa stain. </p>
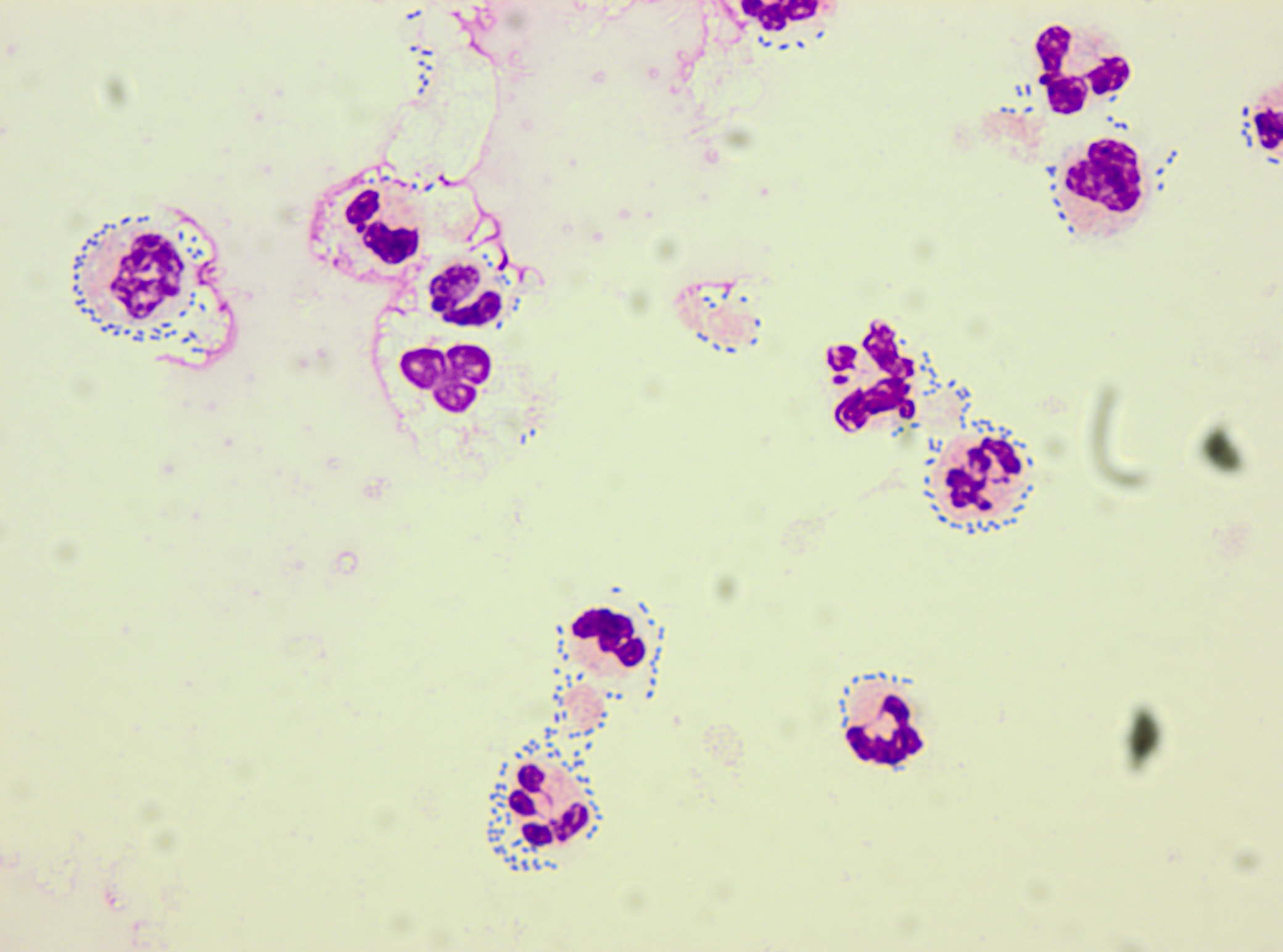
Cytospin prepared from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of a patient with bacterial meningitis. Predominant presence of neutrophil granulocytes and only occasionally monocytes being encountered. Massive presence of extracellular diplococci surrounding WBC. May-Gruenwald Giemsa stain
<p>Cytospin prepared from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of a patient with bacterial meningitis. Predominant presence of neutrophil granulocytes and only occasionally monocytes being encountered. Massive presence of extracellular diplococci surrounding WBC. May-Gruenwald Giemsa stain</p>
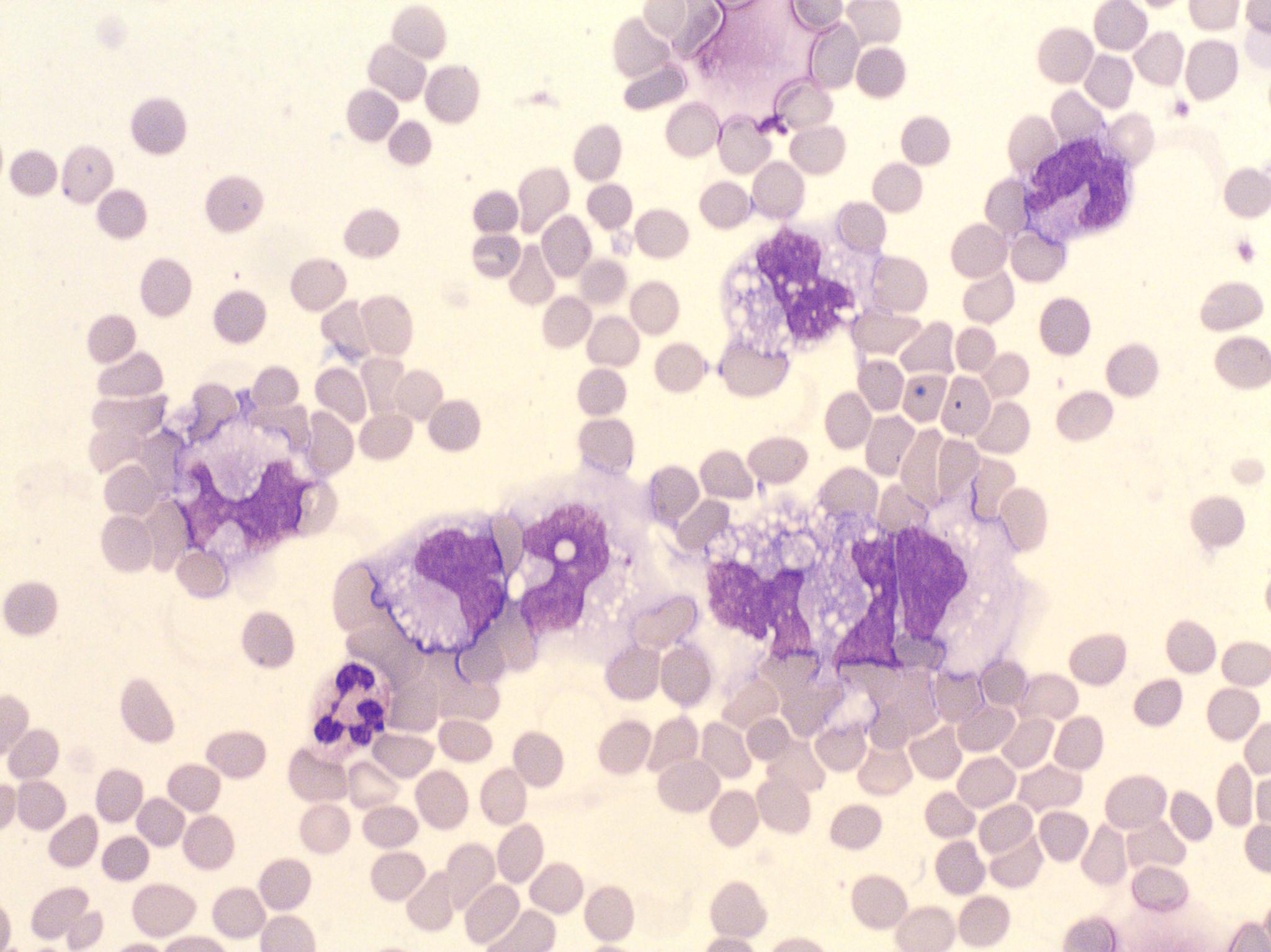
Cytospin prepared from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of a newborn suffering from sepsis. The blood/brain barrier has not yet been closed, so the macrophages that are cleaning up the bacteria in the blood end up also in the CSF. May-Gruenwald Giemsa stain.
<p>Cytospin prepared from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of a newborn suffering from sepsis. The blood/brain barrier has not yet been closed, so the macrophages that are cleaning up the bacteria in the blood end up also in the CSF. May-Gruenwald Giemsa stain.</p>
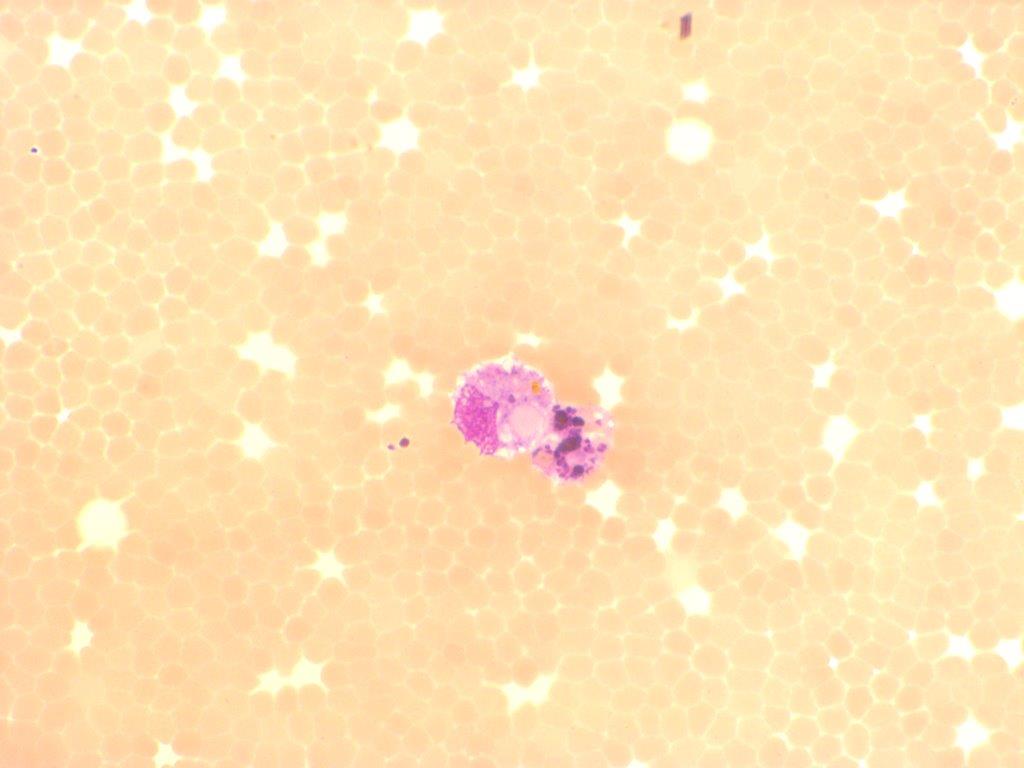
Cytospin prepared from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of a patient with posterior communicating artery (PCoA) aneurysm after six weeks of the incidence. Erythrophages and siderophages with ingested red blood cells. As red blood cells degenerate further, the breakdown products are seen in the phagocytic cells as dark, granular, iron-laden haemosiderin deposits or yellow crystalline iron-free haematoidin crystals. May-Gruenwald Giemsa stain.
<p>Cytospin prepared from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of a patient with posterior communicating artery (PCoA) aneurysm after six weeks of the incidence. Erythrophages and siderophages with ingested red blood cells. As red blood cells degenerate further, the breakdown products are seen in the phagocytic cells as dark, granular, iron-laden haemosiderin deposits or yellow crystalline iron-free haematoidin crystals. May-Gruenwald Giemsa stain. </p>
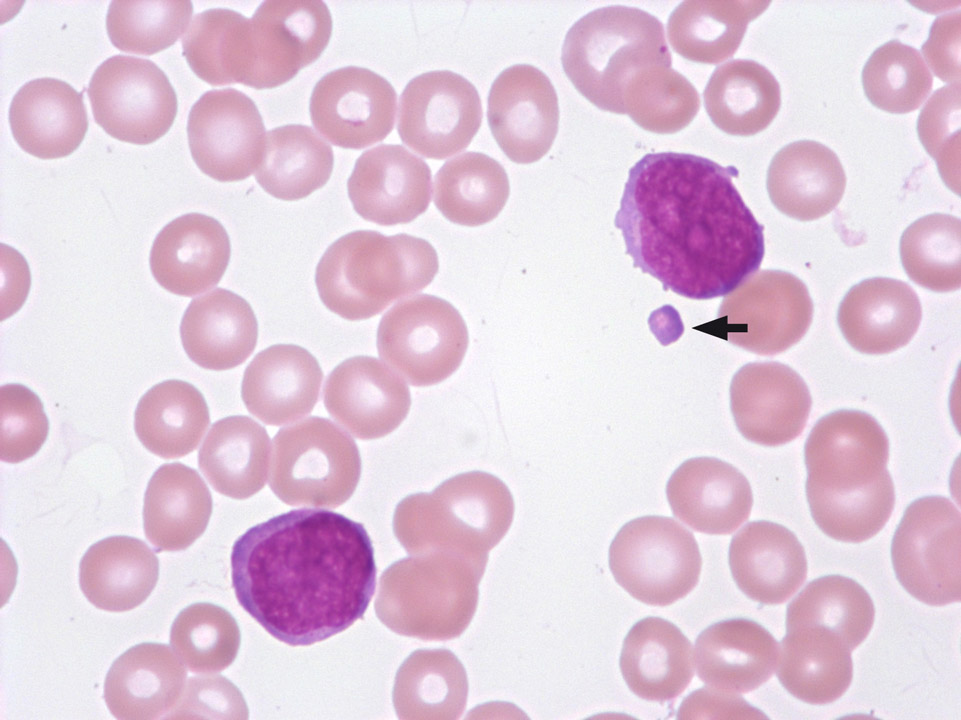
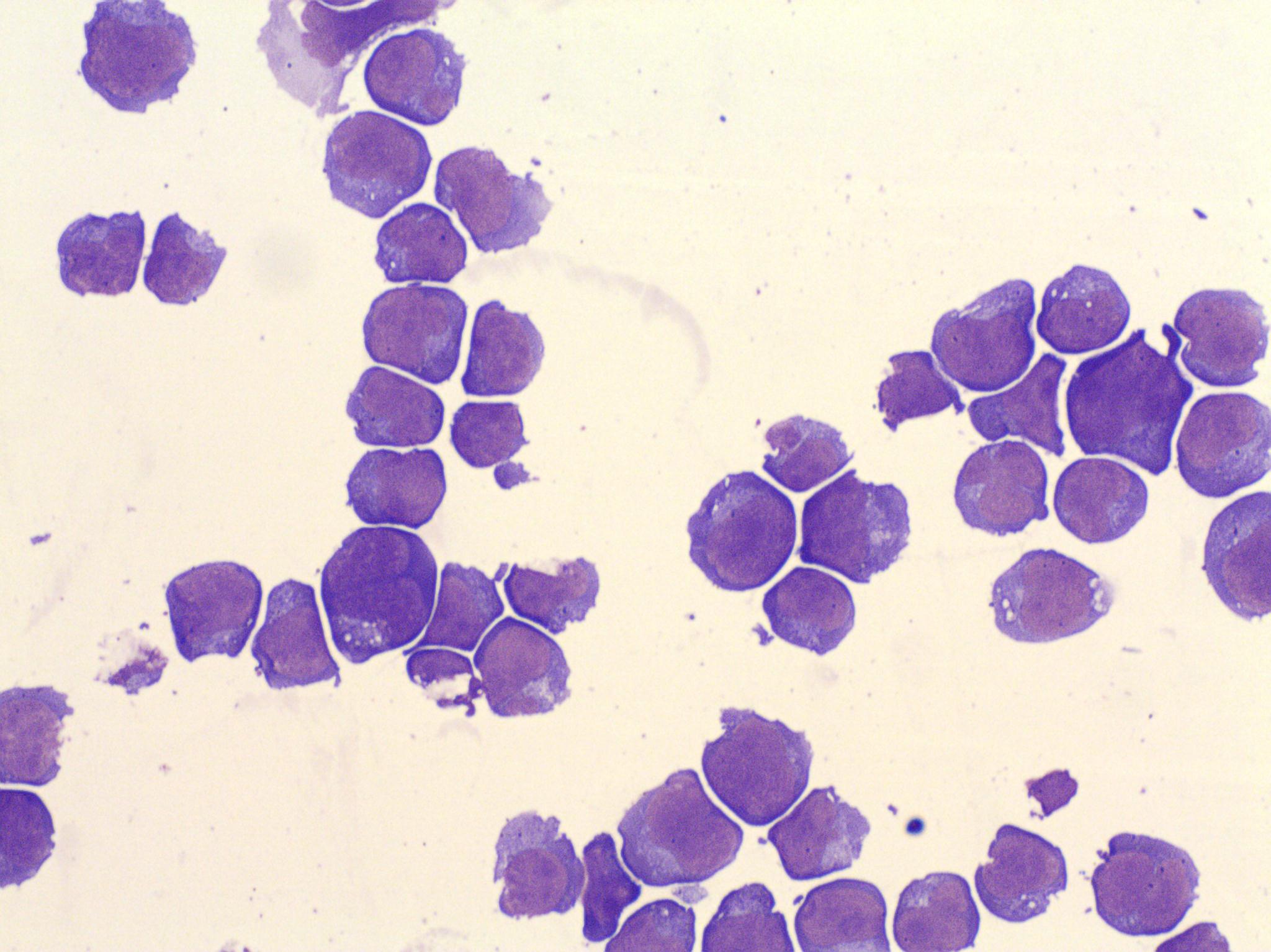
Cytoplasmic fragments split off a blast in a case of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL). In certain automated haematology analysers, such fragments might possibly suggest a wrongly high concentration of platelets.
<p>Cytoplasmic fragments split off a blast in a case of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL). In certain automated haematology analysers, such fragments might possibly suggest a wrongly high concentration of platelets.</p>
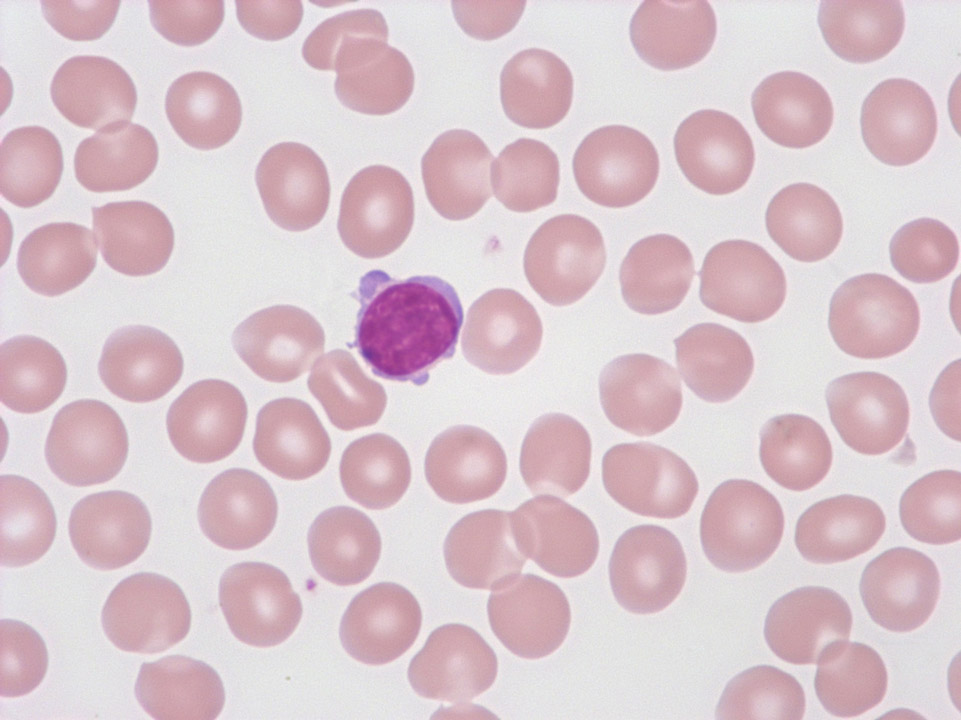
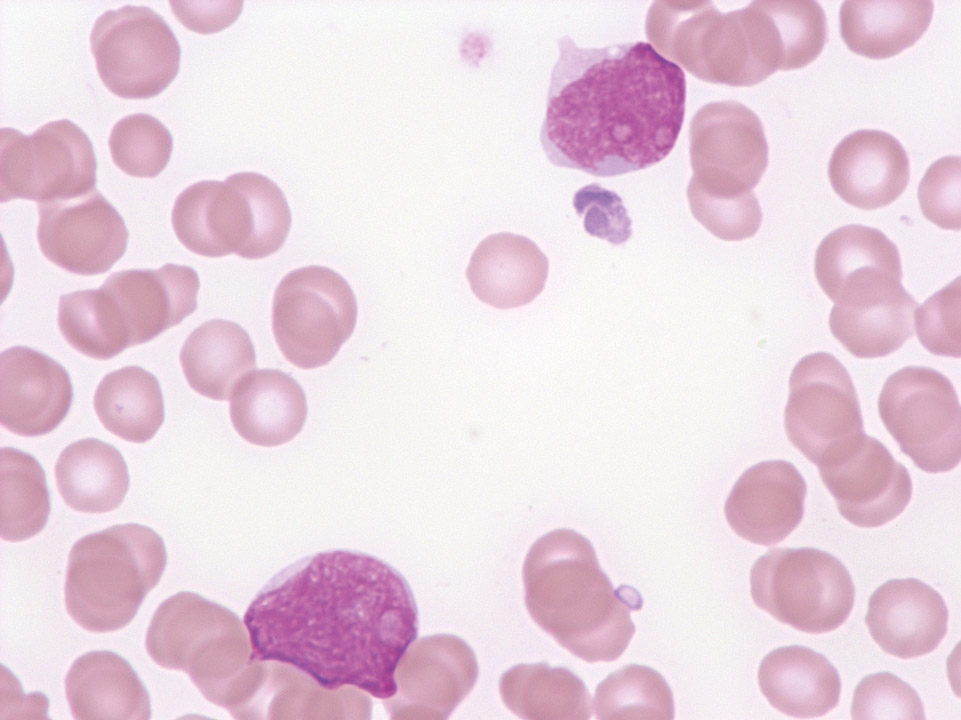
Cytoplasmic protrusions of a lymphocyte in normal blood. (Although such protrusions are frequently found with infections, contrary to activated lymphocytes they are of no diagnostic importance.)
<p>Cytoplasmic protrusions of a lymphocyte in normal blood. (Although such protrusions are frequently found with infections, contrary to activated lymphocytes they are of no diagnostic importance.)</p>