Galeria de imagens
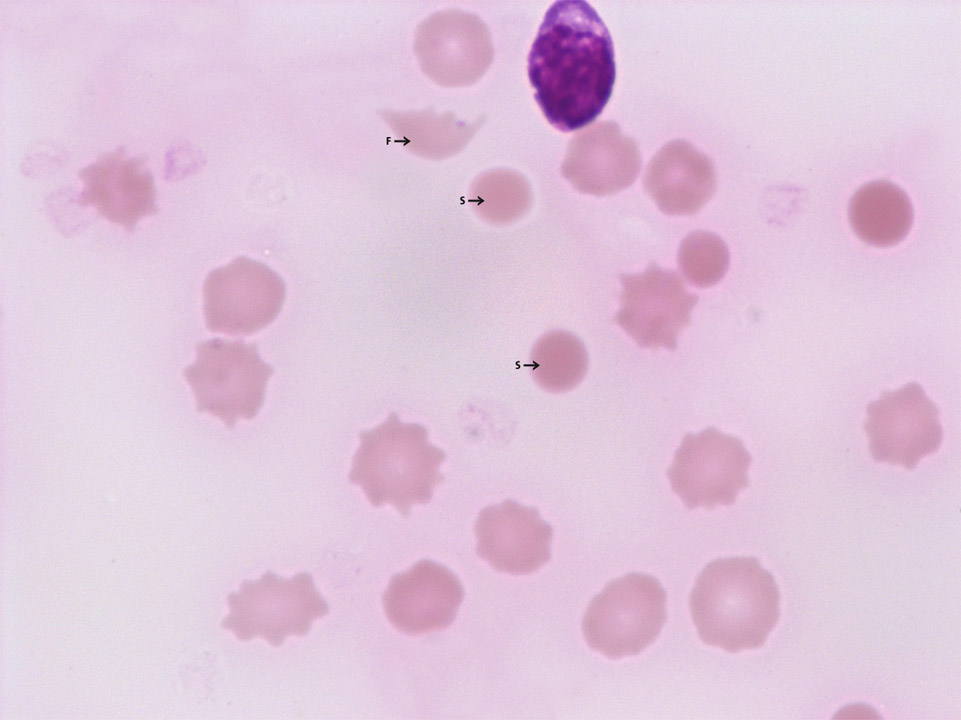
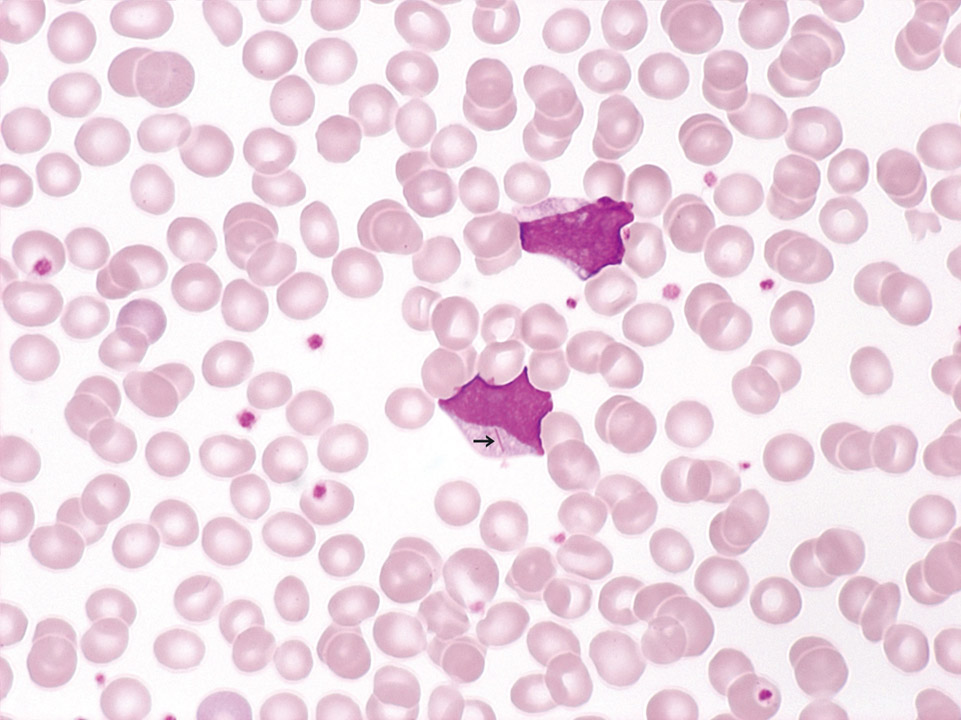
Acute haemolysis: fragmented red cells (F), spherocytes (S) and free haemoglobin (= reddish smears) in a patient with gas gangrene, caused by Clostridium perfringens. (The acanthaceous appearing cells are no acanthocytes but red blood cells on the verge of disintegration.)
<p>Acute haemolysis: fragmented red cells (F), spherocytes (S) and free haemoglobin (= reddish smears) in a patient with gas gangrene, caused by Clostridium perfringens. (The acanthaceous appearing cells are no acanthocytes but red blood cells on the verge of disintegration.) </p>
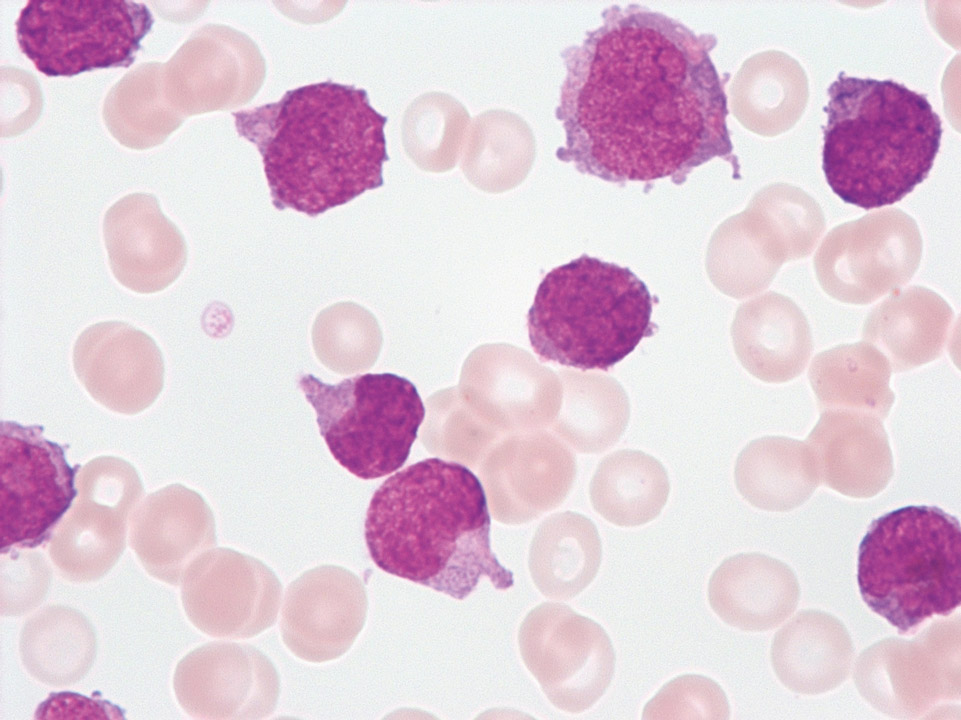
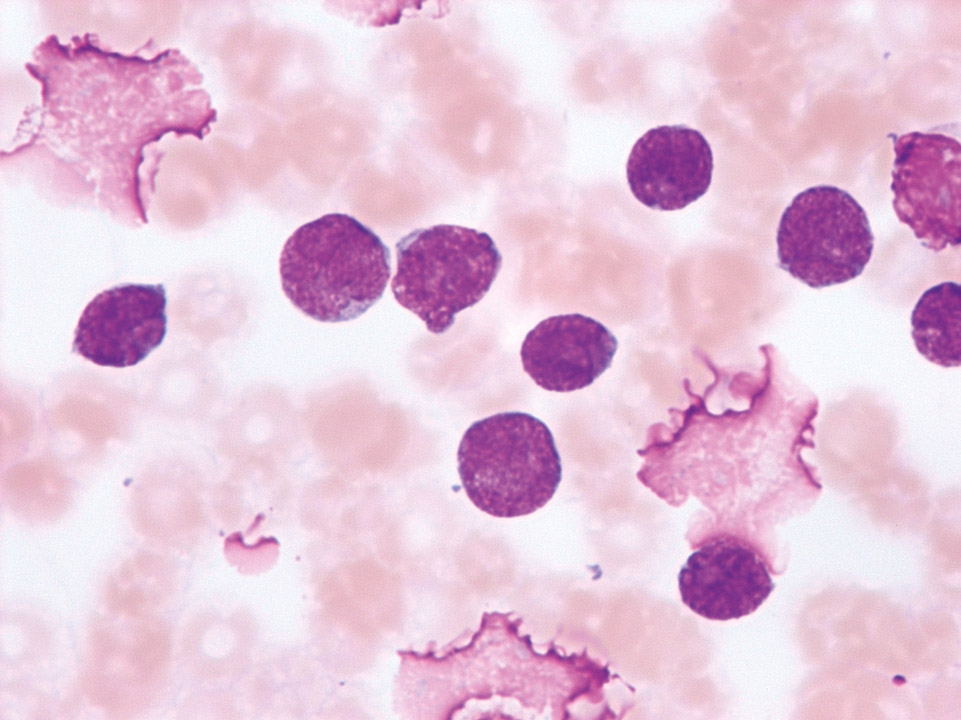
Blasts (33% in total) with Auer rods (->) in the peripheral blood (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) are sufficient proof of an acute myeloid leukaemia (AML).
<p>Blasts (33% in total) with Auer rods (->) in the peripheral blood (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) are sufficient proof of an acute myeloid leukaemia (AML).</p>
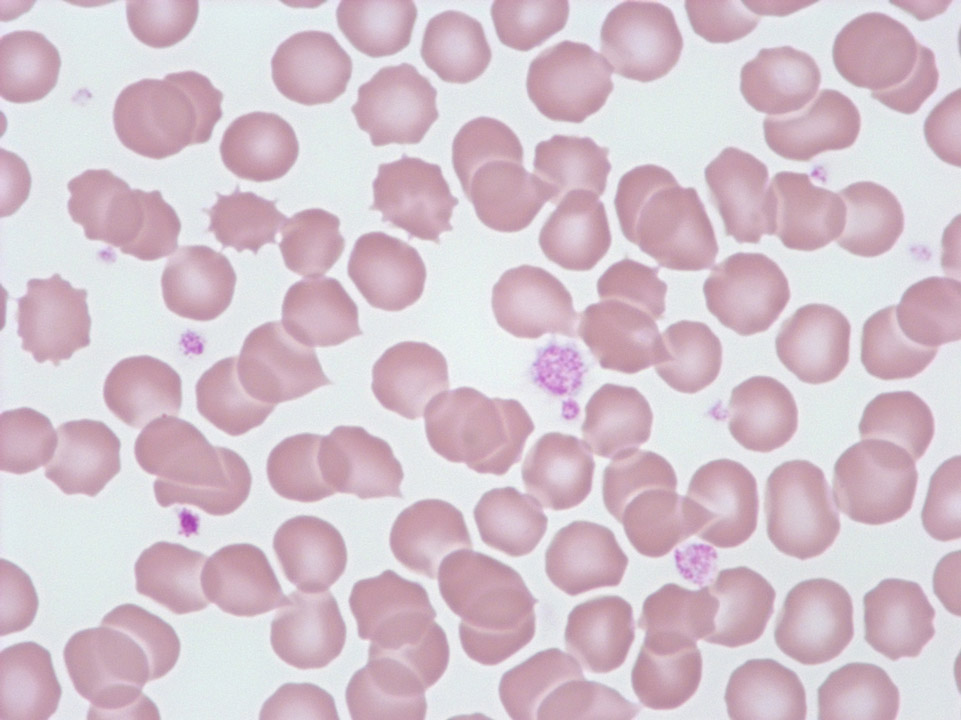
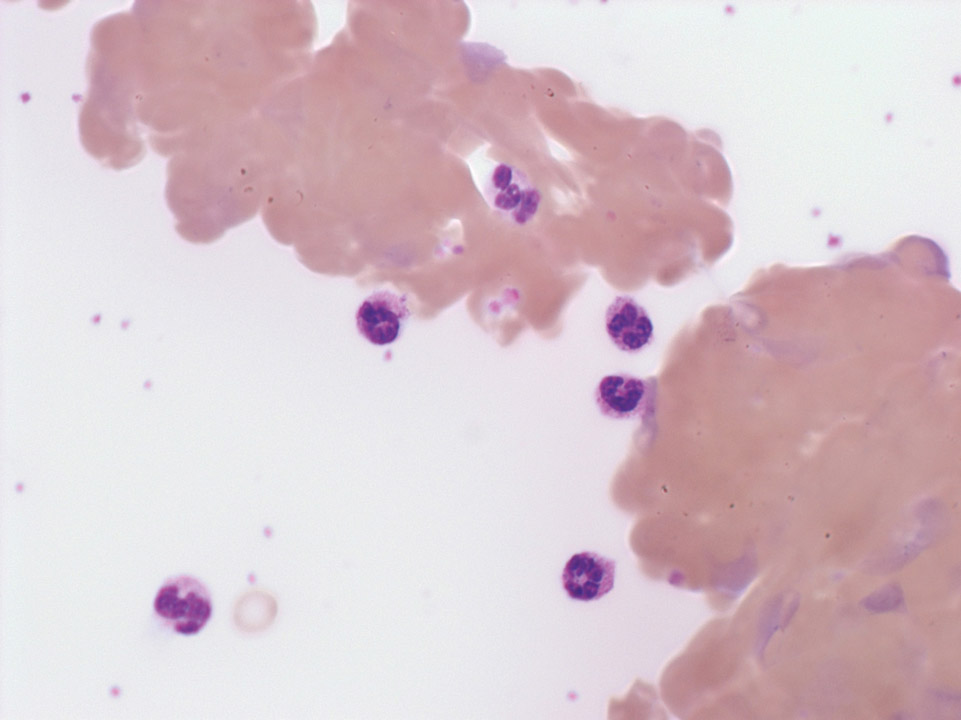
White blood cell concentration 180,000/μL. Despite intensive search no granulocytes were detectable. Diagnosis: acute T lymphoblastic leukaemia
(T-ALL).
<p>White blood cell concentration 180,000/μL. Despite intensive search no granulocytes were detectable. Diagnosis: acute T lymphoblastic leukaemia </p> <p>(T-ALL).</p>
Agglutinated red blood cells and marked polychromasia in a patient with haemolytic anaemia caused by cryoglobulins in Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia.
<p>Agglutinated red blood cells and marked polychromasia in a patient with haemolytic anaemia caused by cryoglobulins in Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia.</p>
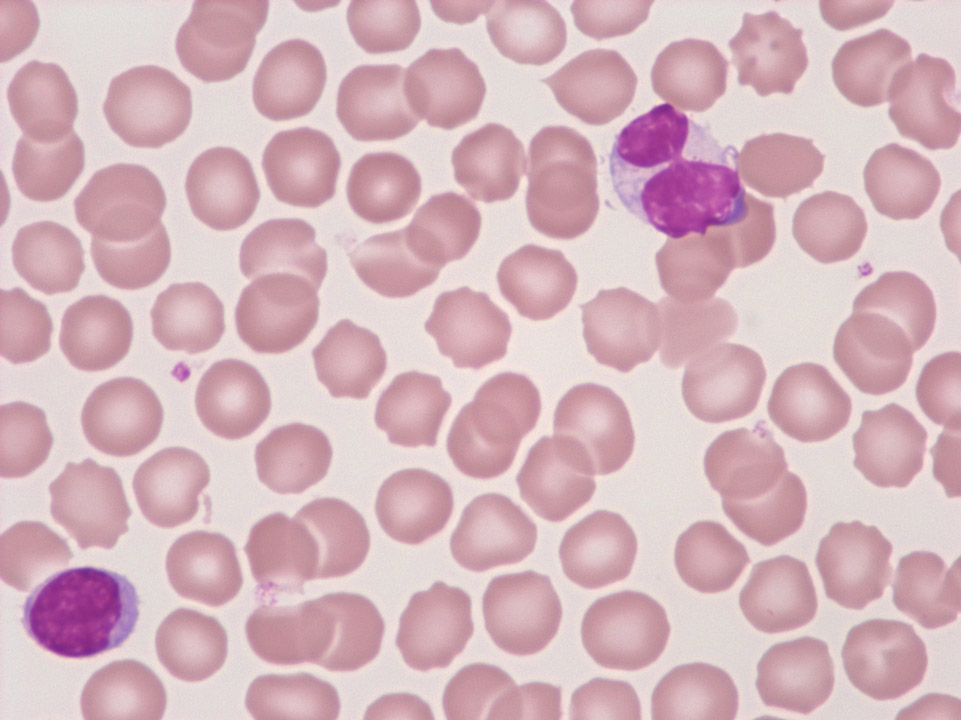
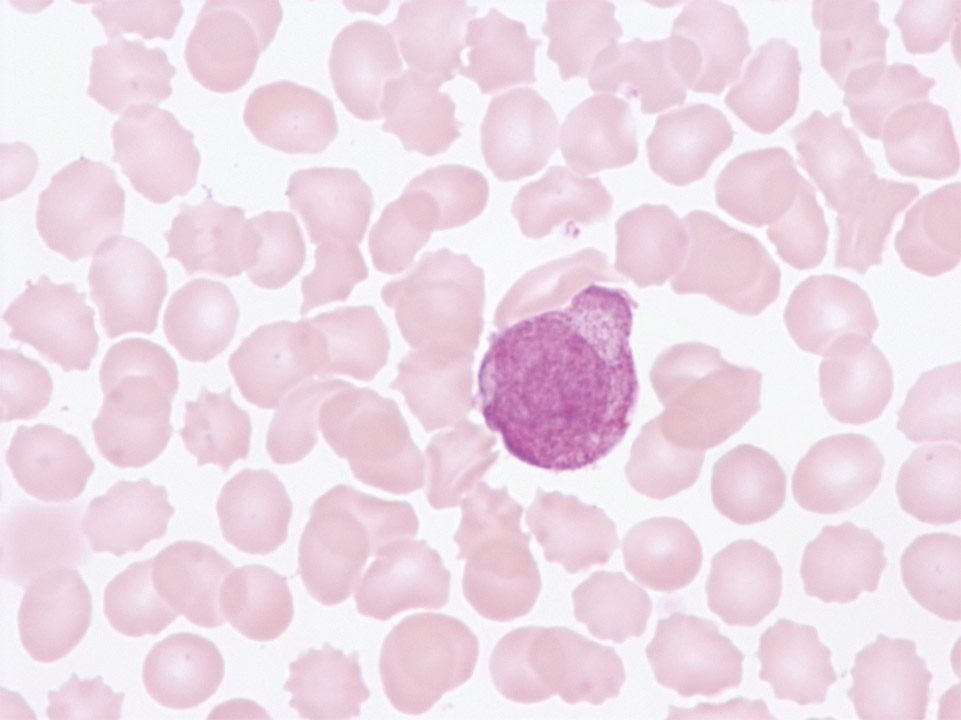
On the top right a morphologically atypical lymphocyte of a healthy individual with the abnormality resulting from prolonged storage of the EDTA blood (24 hours).
<p>On the top right a morphologically atypical lymphocyte of a healthy individual with the abnormality resulting from prolonged storage of the EDTA blood (24 hours).</p>
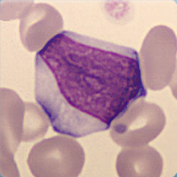
Cell description:
Size: larger than normal lymphocytes
Nucleus: oval, variable chromatin condensation
Cytoplasm: Diffluent, often around red blood cells
<p>Cell description: </p> <p>Size: larger than normal lymphocytes </p> <p>Nucleus: oval, variable chromatin condensation </p> <p>Cytoplasm: Diffluent, often around red blood cells</p>